The economist blockchain technology definition

Wikiversity has learning resources about Blockchain. By decentralizing data on an accessible ledger, public blockchains make block-level data transparent to everyone involved. Archived from the original on 23 March
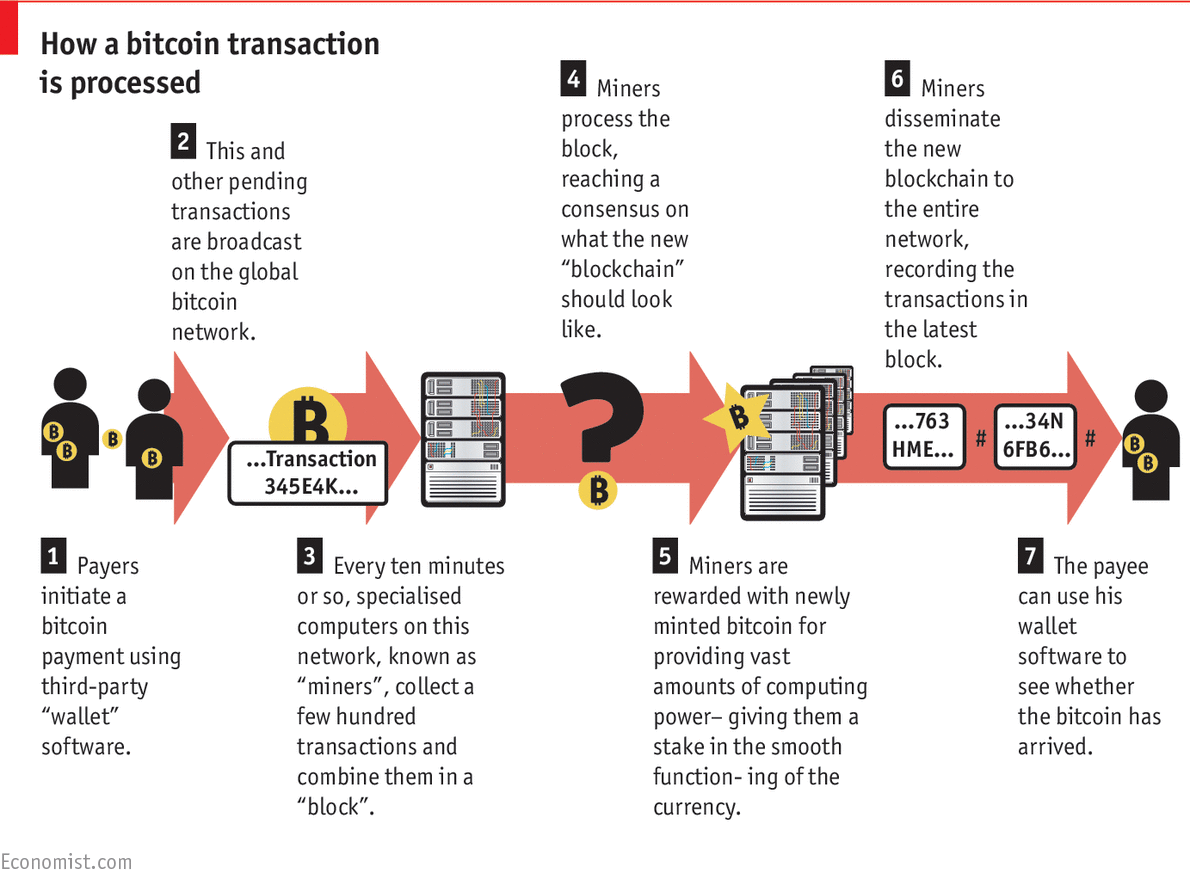
Archived from the original on 19 May Archived from the original on 10 April The use of a blockchain removes the characteristic of infinite reproducibility from the economist blockchain technology definition digital asset. Based on the Bitcoin protocol, the blockchain database is shared by all nodes participating in a system.
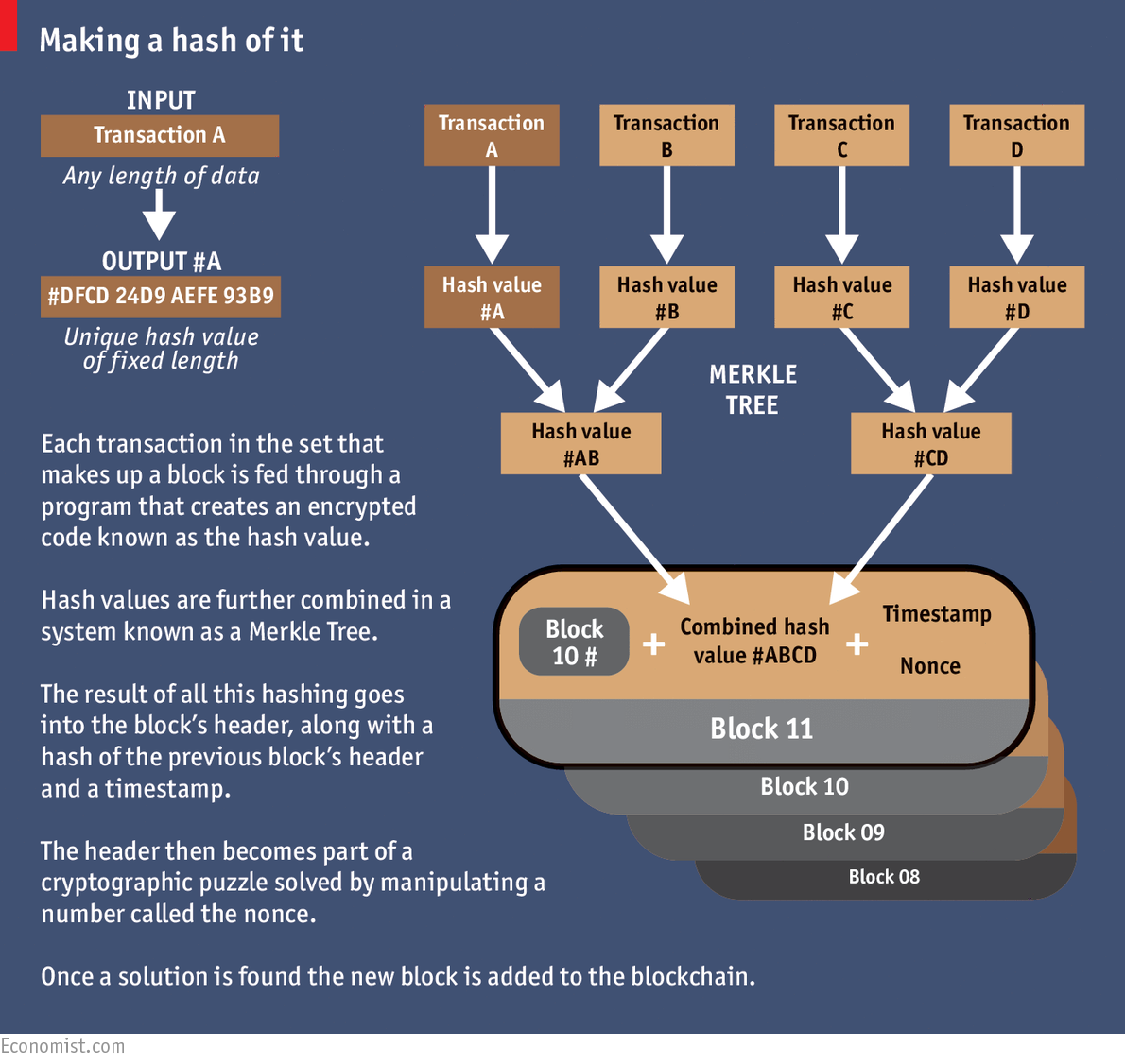
Many banks are partnering with companies building so-called private blockchains that mimic some aspects of Bitcoin's architecture except they're designed to be closed off and accessible only to chosen parties. As of [update]some observers remain skeptical. Archived from the original on 10 October Kodak announced plans in to launch a digital token system for photograph copyright recording.

They automate processes that were previously time-consuming and done manually, such as the incorporation of businesses. Blockchains facilitate users could take ownership of game assets digital assetsan example of this is Cryptokitties. Web browser company Brave uses a blockchain to verify when users the economist blockchain technology definition viewed ads and, in turn, pays publishers when those same users consume content. Archived PDF from the original on 20 March

Archived from the original on 12 January Retrieved 17 November Lakhani said the blockchain is not a disruptive technology that undercuts the cost of an existing business model, but is a foundational technology the economist blockchain technology definition "has the potential to create new foundations for our economic and social systems". A blockchain smart contract would be enabled by extensible programming instructions that define and execute an agreement.
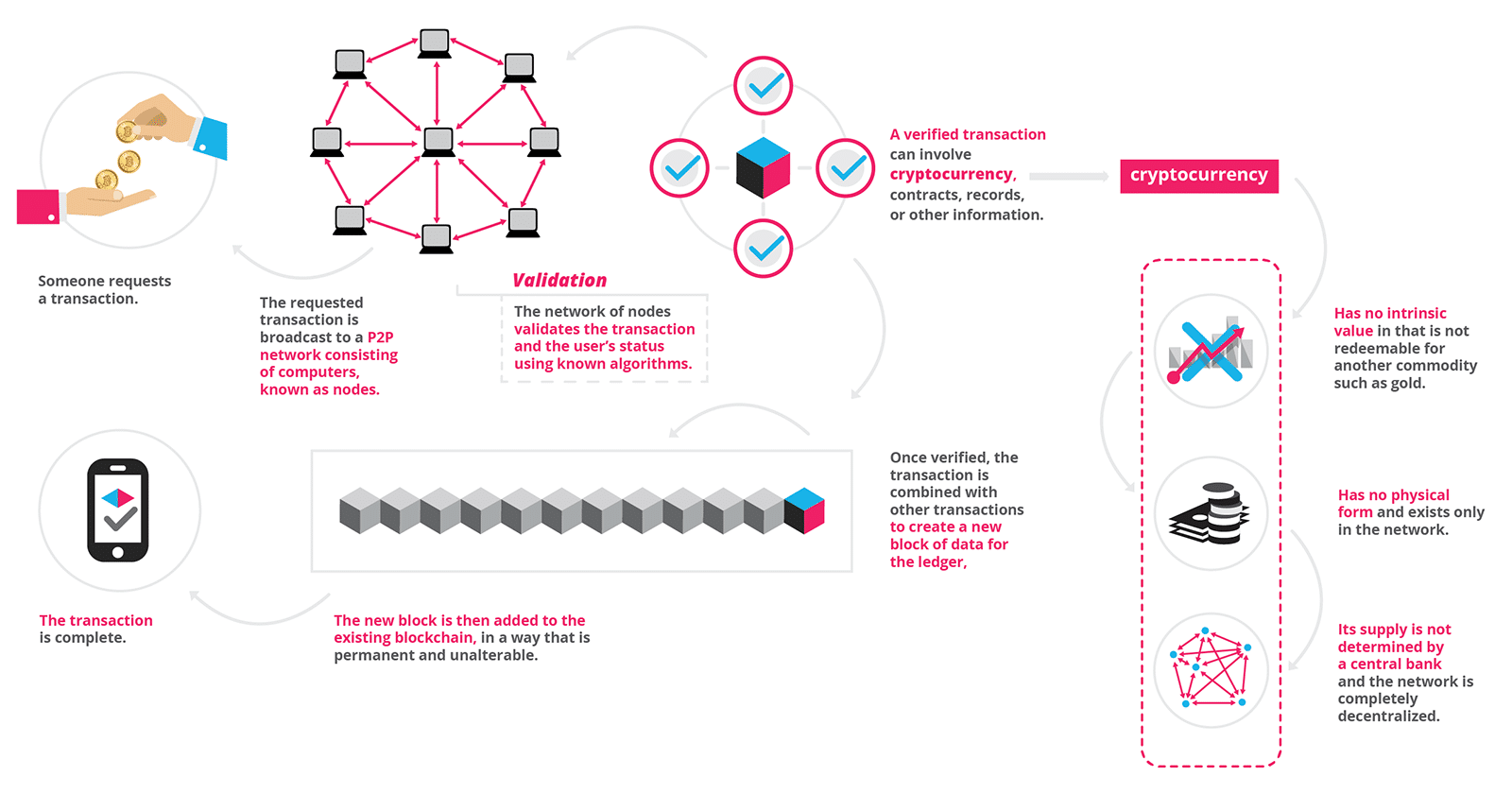
He is an expert in blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, equity crowdfunding, the adoption of technology standards, and science and technology interactions. According to Kugel, by enabling universal data interchange, self-describing data can greatly expand the number of participants in permissioned commercial blockchains without having to concentrate control of these blockchains to a limited number the economist blockchain technology definition behemoths. What if a highway could verify the identity of and accept payment from a self-driving car, opening up a pay-per-use fast lane to commuters in a rush? Self-describing data also facilitates the integration of data between disparate blockchains.
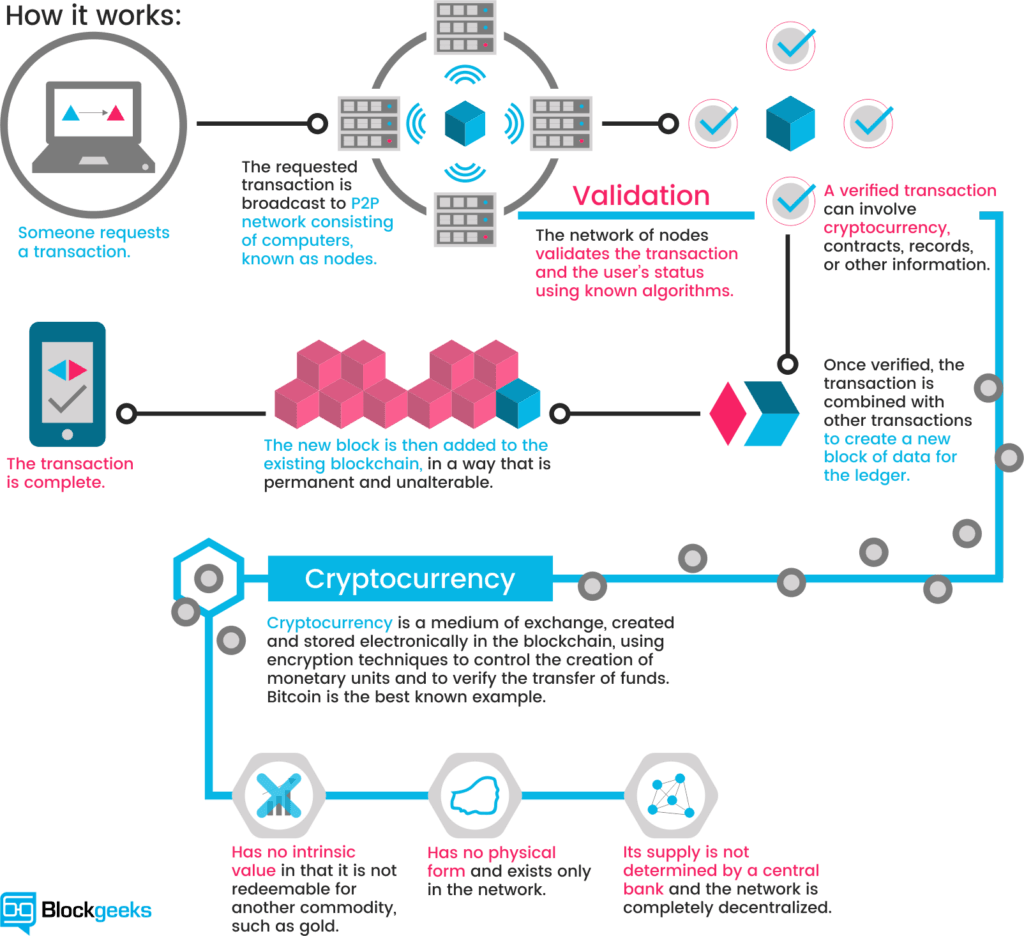
By storing data across its peer-to-peer network, the blockchain eliminates a number of risks that come with data being held centrally. Retrieved 2 November Archived from the original on 11 January There are two types of costs blockchain could reduce for you: Archived from the original on 6 January

Banks are interested in this technology because it has potential to speed up back office settlement systems. An issue in this ongoing debate is whether a private system with verifiers tasked and authorized permissioned by a central authority should be considered the economist blockchain technology definition blockchain. Zcash promises to be a fully private cryptocurrency. Lakhani said the blockchain is not a disruptive technology that undercuts the cost of an existing business model, but is a foundational technology that "has the potential to create new foundations for our economic and social systems".

Some countries, especially Australia, are providing keynote participation in identifying the various technical issues associated with developing, governing and using blockchains:. Value tokens sent across the network are recorded as belonging to that address. But the economist blockchain technology definition to see smaller, developed countries with a high tolerance for technology experimentation lead the way and possibly experiment with a fiat-backed, digital currency for some of their needs.