Medical Definition of Recombinant DNA molecules
5 stars based on
60 reviews
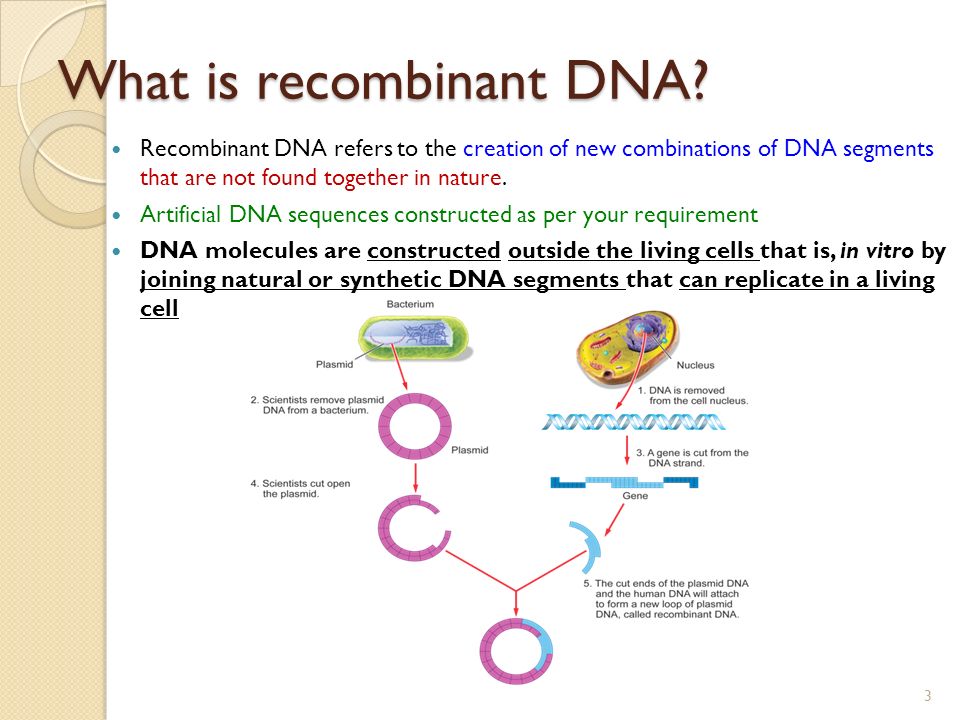
Recombinant DNA technology emerged as a response to the need for specific DNA segments in amounts sufficient for biochemical analysis. The method entails clipping the desired segment out of the surrounding DNA and copying it millions of times. The success of recombinant DNA technology, by which microbial cells can be engineered to produce foreign proteins, relies on recombinant dna molecule definition faithful reading of the corresponding genes by bacterial cell machinery, and has fueled most of the recent advances in modern molecular biology.
During the last twenty years, recombinant dna molecule definition of cloned DNA sequences have given us a detailed knowledge of gene structure and organization, and have provided clues to the regulatory pathways by which the cell controls gene expression in the multiple cell types comprising the basic vertebrate body plan. Genetic engineering, by which recombinant dna molecule definition organism can be modified to include new genes designed with desired characteristics, is now routine practice in basic research laboratories.
It has provided the means to produce large amounts of highly purified normal and mutant proteins for detailed analysis of their function in the organism. Recent advances in recombinant dna molecule definition technology have also changed the course of medical research. Exciting new approaches are being developed to exploit the enormous potential of recombinant DNA research in the analysis of genetic disorders.
The new ability to manipulate human genetic material has opened radically new avenues for diagnosis and treatment, and has far-reaching consequences for the future of medicine.
Molecular cloning provides a means to exploit the rapid growth of bacterial cells for producing large amounts of identical DNA fragments, which alone have no capacity to reproduce themselves. The fragment of DNA to be amplified is first inserted into a cloning vector.
The most popular vectors currently in use consist of either small circular DNA molecules plasmids or bacterial viruses phage. The vectors contain genetic information that allows bacterial DNA replication machinery to copy them. After insertion of the foreign DNA, the plasmid or phage vector is re-introduced into a bacterial cell. The growing bacterial culture replicates the recombinant dna molecule definition DNA, along with the vector, in hundreds of copies per cell.
This process yields multiple, identical clones of the original recombinant molecule. It is easy to harvest vectors from the bacterial culture, and release the amplified foreign DNA fragments with the same restriction enzyme used to insert the original DNA fragment into the vector Figure 4, top. The power of molecular cloning is remarkable: For analysis recombinant dna molecule definition long stretches of DNA, eukaryotic vectors that can grow in yeast have been developed which can hold megabases of foreign DNA.
These vectors mimic yeast chromosomal structure, so that they are replicated along with the native yeast chromosomes every time a yeast cell divides. Yeast Artifical Chromosomes, or YACs, are often the recombinant dna molecule definition way to clone extremely large genes including huge introns all in one continuous piece. YACs also provide a way to propagate DNA in a eukaryotic cell, where DNA modification, an important part of the eukaryotic genetic regulatory machinery, is more likely to be retained more on this later.
YACs are increasingly useful in the many Genome Projects underway, as we aim to understand the metastructure of chromosomes, where the placement and arrangement of genes within the "junk" DNA surrounding them may hold as yet undiscovered regulatory information for packaging and accessibility.
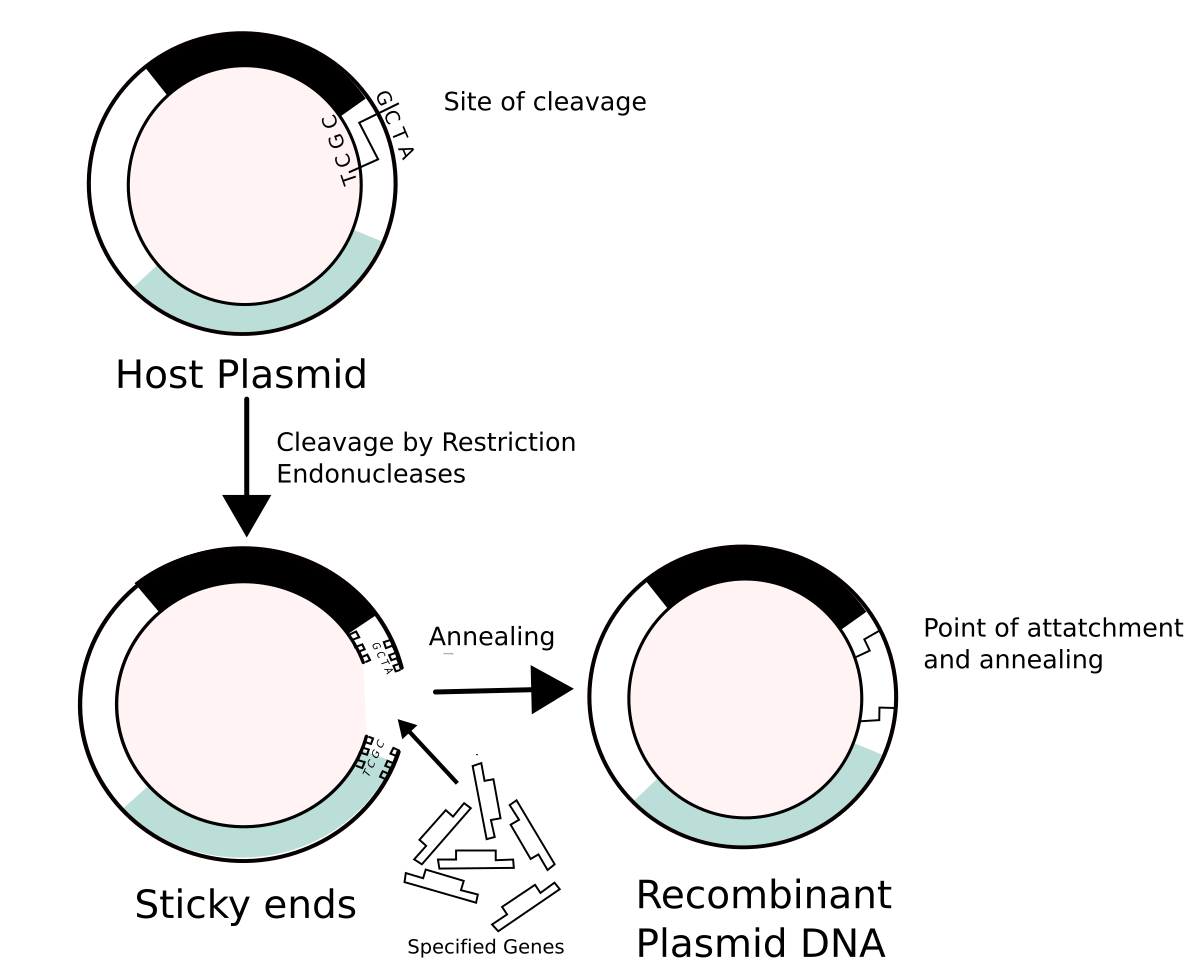
The DNA segment to be amplified is separated from surrounding genomic DNA by restriction enzyme cleavage, which often produces staggered or sticky ends. The plasmid vector brown is prepared to accept the isolated genomic DNA fragment by cutting the circular plasmid DNA at a single site with the same restriction enzyme, generating sticky ends which are complementary to the sticky ends of the genomic DNA fragment.
The cut genomic DNA and the linearized plasmid are mixed together in the presence of recombinant dna molecule definition ligase enzyme, which rejoins the bonds in the DNA backbone on each side of the plasmid-genomic DNA junction. This recombinant DNA molecule is then introduced into bacteria which are able to take up plasmid DNA, and then replicate the plasmid as recombinant dna molecule definition culture grows.