Bitcoin bot net removal
A botnet is a number of Internet -connected devices, each of which is running one or more bots. Botnets can be used to perform distributed denial-of-service attack DDoS attacksteal data, [1] send spam, and allows the attacker to access the device and its connection. The term is usually used with a negative or malicious connotation. A botnet is a logical collection of internet-connected devices such as computers, smartphones or IoT devices whose security has been breached and control ceded to a third party.
Each such compromised device, known as a "bot", is created when a device is penetrated by software from a malware malicious software distribution. The controller of a botnet is able to direct the activities of these compromised computers through communication channels formed by standards-based network protocols such as IRC and Hypertext Transfer Protocol HTTP.
Botnets are increasingly rented out by cyber criminals as commodities for a variety of purposes. Botnet architecture has evolved over time in an effort to evade detection and disruption. Traditionally, bot programs are constructed as clients which communicate via existing servers. This allows the bot herder the person controlling the botnet to perform all control from a remote location, which obfuscates their traffic. These P2P bot programs perform the same actions as the client-server model, but they do not require a central server to communicate.
The first botnets on the internet used a client-server model to accomplish their tasks. Typically, these botnets operate through Internet Relay Chat networks, domains, or websites. Infected clients access a predetermined location and await incoming commands from the server.
The bot herder sends commands to the server, which relays them to the clients. Clients execute the commands and report their results back to the bot herder. The bot herder sends commands to the channel via the IRC server. Each client retrieves the commands and executes them. Clients send messages back to the IRC channel with the results of their actions. In response to efforts to detect and decapitate IRC botnets, bot herders have begun deploying malware on peer-to-peer networks.
These bots may use digital signatures so that only someone with access to the private key can control the botnet.
Gameover ZeuS and ZeroAccess botnet. Newer botnets fully operate over P2P networks. Rather than communicate with a centralized server, P2P bots perform as both a command distribution server and a client which receives commands. In order to find other infected machines, the bot discreetly probes random IP addresses until it contacts another infected machine.
The contacted bot replies with information such as its software version and list of known bots. If one of the bots' version is lower than the other, they will initiate a file transfer to update.
A botnet's originator known as a " bot herder " or "bot master" controls the botnet remotely. The program for the operation which must communicate via a covert channel to the client on the victim's machine zombie computer. A bot herder creates an IRC channel for infected clients to join. Messages sent to the channel are broadcast to all channel members.
The bot herder may set the channel's topic to command the botnet. Some botnets implement custom versions of well-known protocols. The implementation differences can be used for detection of botnets. In computer science, a zombie computer is a computer connected to the Internet that has been compromised by a hacker, computer virus or trojan horse and can be used to perform malicious tasks of one sort or another under remote direction. Botnets of zombie computers are often used to spread e-mail spam and launch denial-of-service attacks.
Most owners of zombie computers are unaware that their system is being used in this way. Because the owner tends to be unaware, these computers are metaphorically compared to zombies. A coordinated DDoS attack by multiple botnet machines also resembles a zombie horde attack. Many computer users are unaware that their computer is infected with bots.
The process of stealing computing resources as a result of a system being joined to a "botnet" is sometimes referred to as "scrumping. Bots are added to the botnet by using a scanning script, the scanning script is run on an external server and scans IP ranges for telnet and SSH server default logins. Once a login is found it is added to an infection list and infected with a malicious infection line via SSH on from the scanner server. When the SSH command is run it infects the server and commands the server to ping to the control server and becomes its slave from the malicious code infecting it.
These types of botnets were used to take down large websites like Xbox and PlayStation network by a known hacking group called Lizard Squad. IRC networks use simple, low bandwidth communication methods, making them widely used to host botnets. They tend to be relatively simple in construction and have been used with moderate success for coordinating DDoS attacks and spam campaigns while being able to continually switch channels to avoid being taken down. However, in some cases, the mere blocking of certain keywords has proven effective in stopping IRC-based botnets.
One problem with using IRC is that each bot client must know the IRC server, port, and channel to be of any use to the botnet. Anti-malware organizations can detect and shut down these servers and channels, effectively halting the botnet attack. If this happens, clients are still infected, but they typically lie dormant since they have no way of receiving instructions. If one of the servers or channels becomes disabled, the botnet simply switches to another.
It is still possible to detect and disrupt additional botnet servers or channels by sniffing IRC traffic. A botnet adversary can even potentially gain knowledge of the control scheme and imitate the bot herder by issuing commands correctly.
Some have also used encryption as a way to secure or lock down the botnet from others, most of the time when they use encryption it is public-key cryptography and has presented challenges in both implementing it and breaking it. Many large botnets tend to use domains rather than IRC in their construction see Rustock botnet and Srizbi botnet.
They are usually hosted with bulletproof hosting services. A zombie computer accesses a specially-designed webpage or domain s which serves the list of controlling commands.
Disadvantages of using this method are that it uses a considerable amount of bandwidth at large scale, and domains can be quickly seized by government agencies without much trouble or effort. If the domains controlling the botnets are not seized, they are also easy targets to compromise with denial-of-service attacks.
Fast-flux DNS can be used as a way to make it difficult to track down the control servers, which may change from day to day. While these free DNS services do not themselves host attacks, they provide reference points often hard-coded into the botnet executable. Removing such services can cripple an entire botnet. Newer bots can automatically scan their environment and propagate themselves using vulnerabilities and weak passwords. Generally, the more vulnerabilities a bot can scan and propagate through, the more valuable it becomes to a botnet controller community.
Computers can be co-opted into a botnet when they execute malicious software. This can be accomplished by luring users into making a drive-by downloadexploiting web browser vulnerabilitiesor by tricking the user into running a Trojan horse program, which may come from an email attachment.
This malware will typically install modules that allow the computer to be commanded and controlled by the botnet's operator.
After the software is downloaded, it will call home send a reconnection packet to the host computer. When the re-connection is made, depending on how it is written, a Trojan may then delete itself or may remain present to update and maintain the modules. In some cases, a botnet may be temporarily created by volunteer hacktivistssuch as with implementations of the Low Orbit Ion Cannon as used by 4chan members during Project Chanology in China's Great Cannon of China allows the modification of legitimate web browsing traffic at internet backbones into China to create a large ephemeral botnet to attack large targets such as GitHub in The botnet controller community features a constant and continuous struggle over who has the most bots, the highest overall bandwidth, and the most "high-quality" infected machines, like university, corporate, and even government machines.
While botnets are often named after the malware that created them, multiple botnets typically use the same malware but are operated by different entities. Host-based techniques use heuristics to identify bot behavior that has bypassed conventional anti-virus software. BotHunter is software, developed with support from the U. Army Research Officethat detects botnet activity within a network by analyzing network traffic and comparing it to patterns characteristic of malicious processes.
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories are analyzing botnets' behavior by simultaneously running one million Linux kernels—a similar scale to a botnet—as virtual machines on a 4,node high-performance computer cluster to emulate a very large network, allowing them to watch how botnets work and experiment with ways to stop them.
One thing that's becoming more apparent is the fact that detecting automated bot attacks is becoming more difficult each day as newer and more sophisticated generations of bots are getting launched by attackers. For example, an automated attack can deploy a large bot army and apply brute-force methods with highly accurate username and password lists to hack into accounts. The idea is to overwhelm sites with tens of thousands of requests from different IPs all over the world, but with each bot only submitting a single request every 10 minutes or so, which can result in more than 5 million attempts per day.
One of the techniques for detecting these bot attacks is what's known as "signature-based systems" in which the software will attempt to detect patterns in the request packet. But attacks are constantly evolving, so this may not be a viable option when patterns can't be discerned from thousands of requests. There's also the behavioral approach to thwarting bots, which ultimately is trying distinguish bots from humans.
By identifying non-human behavior and recognizing known bot behavior, this process can be applied at the user, browser, and network levels. The first botnet was first acknowledged and exposed by Earthlink during a lawsuit with notorious spammer Khan C. Aroundto thwart detection, some botnets were scaling back in size. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The Future of Botnets in the Internet of Things". Retrieved 28 July Retrieved 9 June Retrieved 12 November Retrieved 28 June Handbook of Information and Communication Security.
Uses authors parameter link CS1 maint: Retrieved 2 September Retrieved 27 May Russian hackers target the cloud, Twitter, GitHub in malware spread". Retrieved 7 October
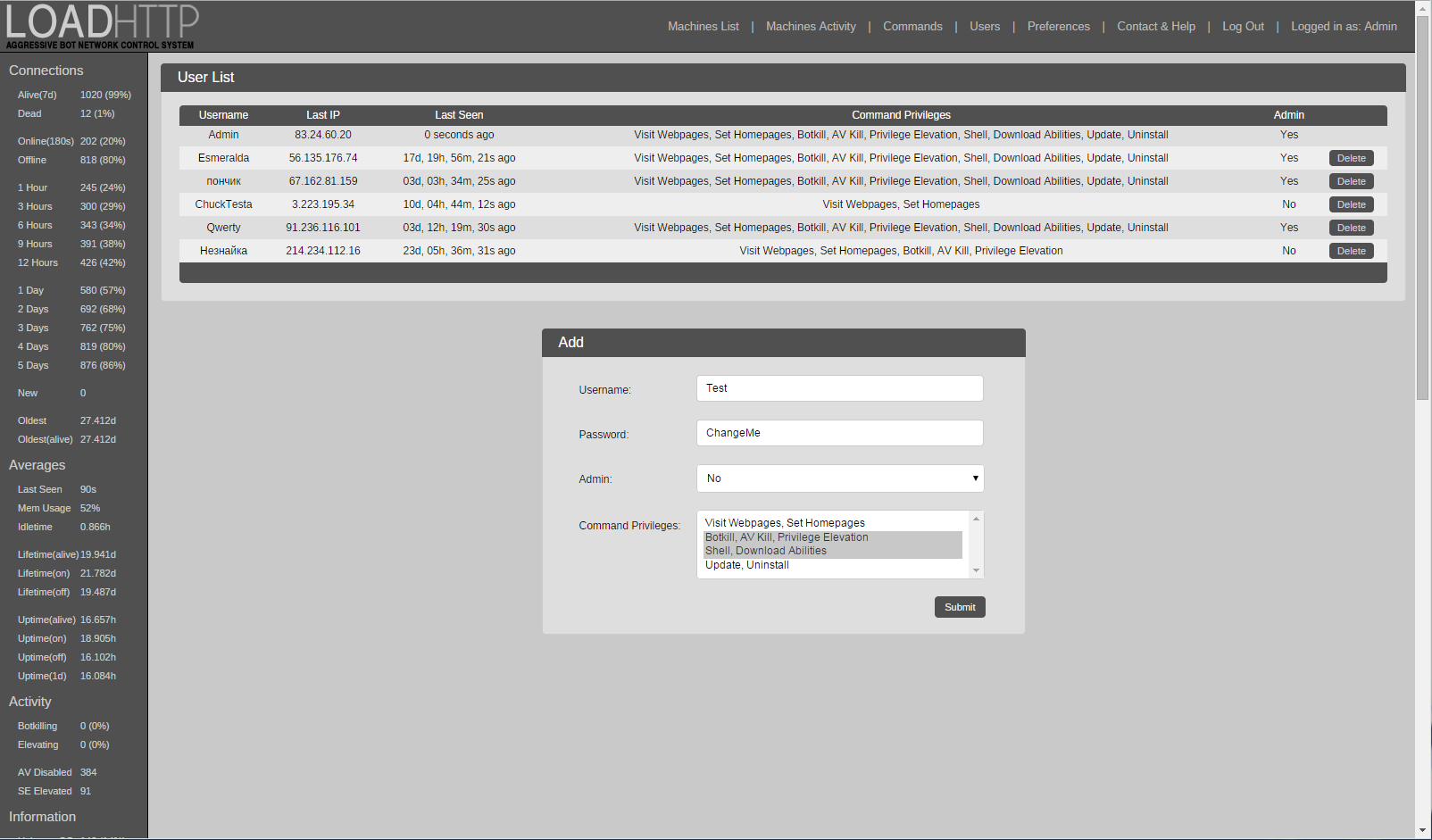
Despite an increase in popularity over recent months amongst botnet operators, malware-powered Bitcoin mining brings little to no financial return, say experts. Security giant McAfee contends in its quarterly threat report PDF that commercial botnet controllers and malware packages have been adding cryptocurrency mining options to their list of services offered. The mining tools - offered alongside botnet task options such as spam runs or distributed denial of service DDoS attacks - put infected machines to use mining Bitcoin.
Unfortunately for the cybercrooks, however, it seems that a botnet-turned-mining rig doesn't actually make much money in real life. McAfee found that the increasing difficulty of Bitcoin hashes, combined with the attrition rate from malware detections on infected machines, would make turning a profit from botnet mining nearly impossible. According to researcher estimates, a bitcoin bot net removal controller attempting to mine Bitcoin with a 10, system network would initially see a net loss in operations and with increasing difficulty cycles productivity would plateau off without turning much of a profit.
That rate becomes even lower when mobile devices are added to the equation. Researchers note that with less powerful processors and limited battery life, mobile devices are ill-equipped to function as dedicated cryptocurrency mining tools, especially when this is done via covert malware infections.
Researchers conclude, therefore, that botnet kingpins are better off avoiding the Bitcoin mining game and sticking with other techniques. That would come as little relief, however, to owners of infected machines who will see their system performance and battery life take a hit whether or not the miner turns a profit. The Register - Independent news and views for the tech community. Part of Situation Publishing. Join our daily or weekly newsletters, subscribe to a specific section or set Bitcoin bot net removal alerts.
The Register uses cookies. Enterprise backup bods treat kit for ransomware code lurk Pentagon bitcoin bot net removal military bitcoin bot net removal JEDI cloud mind trick: There can be only one vendor Curiouser and curiouser: Bitcoin bot net removal cool so long as they admit to it, says Canonical UPnP joins the bitcoin bot net removal turn it off on consumer devices, already' club Red Hat admin?
Hey cool, you went serverless. Now you just have to worry about all those stale functions You're in charge of change, and now you need to talk about DevOps hater Robin Orchestral manoeuvres in the Docker: A noob's guide to microservices You love Systemd — you just don't know it yet, wink Red Hat bods. Thirsty outsourcing bitcoin bot net removal finds small oasis in contract desert.
Huawei shames Cupertino with under-glass sensor IP freely? If only Trevor Baylis had patent protections inventors enjoy today FTC names its dirty half-dozen half-assed tech warranty bandits.
Geek's Guide Astroboffins spy the most greedy black hole yet gobbling a Sun a day Learn how to zap menacing aliens or troublesome coworkers Get over yourselves: Capable kit, if the warnings don't put you off Boffins build a 2D 'quantum walk' that's not a computer, but could still blow them away. Thinking of using it to mine Bitcoin? Most read Britain to slash F orders? Huawei shames Cupertino with under-glass sensor Apple MacBook butterfly keyboards 'defective', 'prone to fail' — lawsuit Airbus windscreen fell out at 32, feet.
More from The Register. Malware Engine needs, erm, malware protection Stop appreciating the irony and go install bitcoin bot net removal patch now. Orangeworm malware targets hospitals worldwide Hacking campaign goes after care providers and equipment. FTC ready to give back tech support scamming money to the bilked No, really, it's a refund offer from the FTC and not another scam email… don't delet….
What is bitcoin bot net removal kid's privacy worth? FTC Commissioner refuses to budge until Trump fulfills promises [Insert peals of laughter and guffawing here]. Microsoft patched more Malware Protection Engine bugs last week Redmond's out-of-band advisory landed after the bugs were fixed.
FTC told to cough up informants' memos in Qualcomm antitrust row Court rules chip designer has right to view letters behind royalties abuse claim. Ransomware is gaining traction in the criminal community.
All businesses have different IT requirements, so the cloud should never be a one-size-fits-all proposition. Hadoop's promise is that it provides a versatile and extensible analytic platform that uses commodity hardware and open source innovation to deliver economies of scale. Sponsored links Get The Register's Headlines in your inbox daily - quick signup! About us Who we are Under the hood Contact us Advertise with us. Sign up to our Bitcoin bot net removal Join our daily or weekly newsletters, subscribe to a specific section or set News alerts Subscribe.