The Power of Schnorr: The Signature Algorithm to Increase Bitcoin's Scale and Privacy
4 stars based on
72 reviews
Software bitcoin ecdsa signature size of ECDSA may be susceptible to side-channel attacks that leak information about the private key. Luckily, the latest generation devices are equipped with specialized hardware that supports key generation and signing, but leveraging bitcoin ecdsa signature size new features for existing blockchains is not straightforward because of the different algorithms involved.
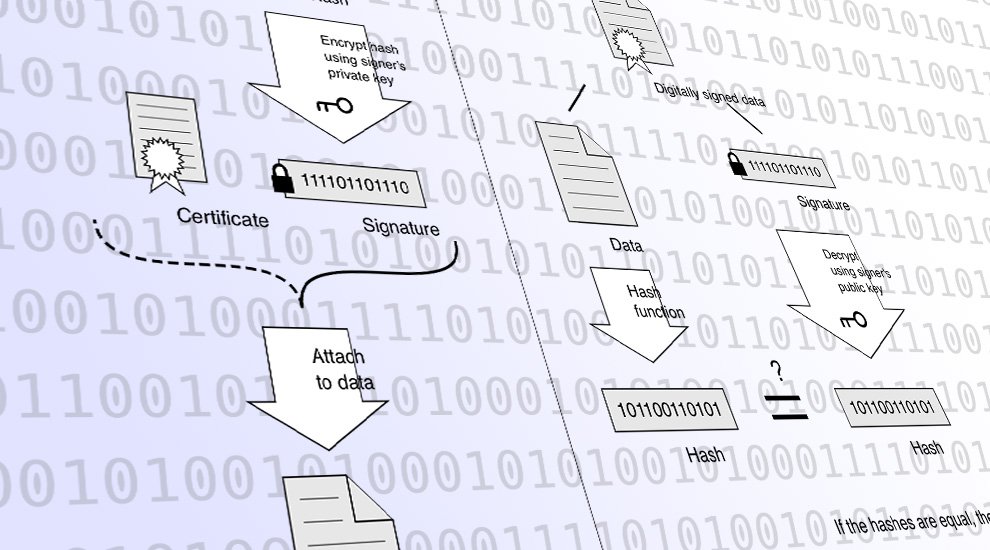
A cryptographic signature proves that the sender of the transaction had access to a private key and that the transaction has not been changed since it was signed. This pair of integers is added to the transaction data to create a signed transaction and then broadcast to the blockchain network.
The miners on the network then check the transaction details whether you actually have money to spend, for example and verify the ECDSA signature to ensure that the sender, identified by a public key, has had access to the corresponding private key. Multiple transactions are combined into a block, including a reference to the previous block, creating a chain of blocks. The security of your funds or smart contracts depends on the security of your private key s.
There are several popular ways for securing bitcoin ecdsa signature size private keys to ensure they cannot be copied or stolen:.
A Key Derivation Function generates a private key from a secret value such as a password or passphrase. However, the derivation algorithm itself can leak side-channel information that reveals the private key. With hardware signing, the private key resides in the hardware and cannot be retrieved. It can only be used to calculate signatures. The private key and any temporary values calculated during signing reside in hardware registers and are not stored in memory or accessible from software.
Of course, having unprotected access to the hardware would allow an attacker to sign malicious transactions all the same, without knowing the private key, so this method and KDF are often combined, with the derivation of the key happening in hardware as well.
The latest Android and iOS devices support hardware signing on a specifically designed hardware component bitcoin ecdsa signature size the Secure Element. This is indeed the reason why all cryptocurrency wallet apps are bitcoin ecdsa signature size software signing. Similarly, many of the hardware solutions mentioned earlier do not support the blockchain curve either.
Feel free to skip to the next section Curve Parameters. An Elliptic Curve is an algebraic curve defined by the equation: In the context of Elliptic Curve Cryptography, a private key is simply a random positive integer, typically identified with the letter d. The corresponding public key, identified by Qis actually a point on the curve with coordinates Qx,Qy.
The coordinates of the base point Gx,Gy are also a constant and are chosen as to generate unique values with each subsequent addition. Multiplication of a point by an integer multiplication by a scalar is no different than applying addition multiple times.
What this means is that the all the values in the calculations are limited to use values from a finite set of numbers. In particular, for bit ECC, all the parameters are bitcoin ecdsa signature size to be from the set of positive integers smaller than some big number pwhere p itself must be smaller than 2 in order to make every value fit within bits of storage.
There are many elliptic curves, with different parameters, that are bitcoin ecdsa signature size used for cryptographic purposes. As mentioned before, the different hardware solutions support multiple curves, but usually do not bitcoin ecdsa signature size secpk1. Instead, they include support for a curve called secpr1also known as prime The question why these hardware solutions are using this particular curve and not the other popular one is a source of many conspiracy theories.
A point calculated with one set of parameters would simply not lie on the curve represented by the other set. A public key calculated by secpr1 hardware would not be a valid public key for use with Bitcoin, for example. We could still rely on the hardware backed APIs to evaluate the key derivation function and as a source of high-quality randomness.
But having to run the signature calculation in software may expose the private key to side channel attacks from other programs running on the same bitcoin ecdsa signature size, even across bitcoin ecdsa signature size machines.
But even when the underlying hardware supports custom curves, the SDKs do not necessarily give 3rd party developers access to all these functions and usually limit ECDSA to secpr1. This is currently the case for both Android and iOS. We can however sign transactions indirectly: Without dedicated secpk1 hardware support we are stuck with signing transactions in software.
In the case of Ethereum, however, we have at our disposal a Turing-complete secure virtual machine. We can verify the hardware signature bitcoin ecdsa signature size the virtual machine, no matter what signing algorithm was used to calculate it, as long bitcoin ecdsa signature size we can code up an implementation of the verification algorithm to run inside the Ethereum virtual machine.
Implementations of the ECDSA verification algorithm are a dime a dozen and too many to enumerate here. Although, the fact that the code does not declare the constant a from the list is a solid hint. Bitcoin ecdsa signature size usual, the devil is in the details. From the curve parameters you can see that for the secpk1 curve the parameter a is 0.
The algorithm in the ecc. And this optimization is not unique to this code. Changing their constants bitcoin ecdsa signature size one curve to the other does not work. What is needed is an algorithm that is generic enough to be applicable to all curves, yet still contains the usual optimizations that make ECDSA feasible in the first place.
Furthermore, the code must be general enough to allow for easy porting to a language that Ethereum bitcoin ecdsa signature size. It would make sense to port the Python code to Serpent, since the Serpent programming language was based on Python in the first place, but lately a lot of the tooling around Ethereum is being built for the newer Solidity programming language, a JavaScript lookalike.
Alas, when we tried two months ago, the Solidity compiler could not handle the ported algorithm and the compiler consistently threw an exception on a not-implemented code path deep within its optimizer. We were stuck with the older, less feature filled, Serpent compiler. Simply include the below ABI spec into your contract and you can call it from your own code. The Wcurve contract ABI definition can be found below. Note that this ABI definition can be reused for bit curves other than secpr1.
We encourage everyone to leverage our Wcurve contract to add secpr1 support to their own contracts. This attack was used to retrieve the key from a Trezor hardware wallet: Bitcoin ecdsa signature size the Key Derivation Function and the hardware signing algorithm rely on random numbers. This is another functionality that needs to be provided by hardware. Atmel ECC-based devices http: Infineon Security controllers http: NXP Secure authentication microcontroller http: Recommended Elliptic Curve Domain Parameters http: Original Python wcurve project page http: Miscellaneous Ethereum built-ins http: Cryptographic Signatures A cryptographic signature proves that the sender of the transaction had access to a private key and that the transaction has not been changed since it was signed.
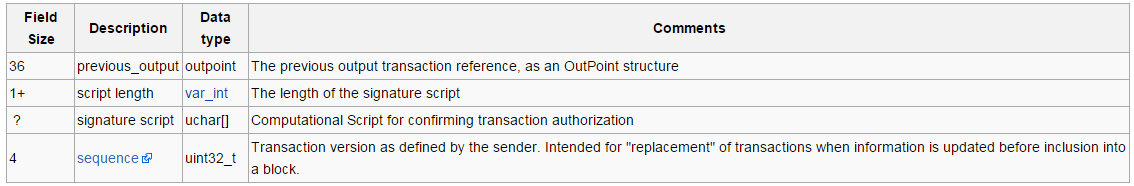
Bitcoin ecdsa signature size with 1 size byte f8 Size of RLP structure 6d Transaction nonce 21 RLP length of gas price 85 Gas price 0ba43b RLP length of gas limit 83 Gas limit 2fefd8 RLP length of address 94 Destination address eaad77a7cada 01a0 RLP length of value 88 Value Wei 0de0b6b3a Extra data none 80 Pubkey recovery bitcoin ecdsa signature size 1b RLP length of r a0 c36fdbfa64aee81da4de7f04def4 77b9aafad07fb2 Value or r RLP length of s a0 4aedfd1d9db40ef02bc3da0a fdecb29 Value or s Signed Ethereum transaction Ether transfer ; ECDSA signature in red hover for info The miners on the network then check bitcoin ecdsa signature size transaction details whether you actually have money to spend, for example and verify the ECDSA signature to ensure that the sender, identified by a public key, has had access to the corresponding private key.
There are several popular ways for securing your private keys to ensure they cannot be copied or stolen: Curve Parameters There are many elliptic curves, with different parameters, that are being used for cryptographic purposes.