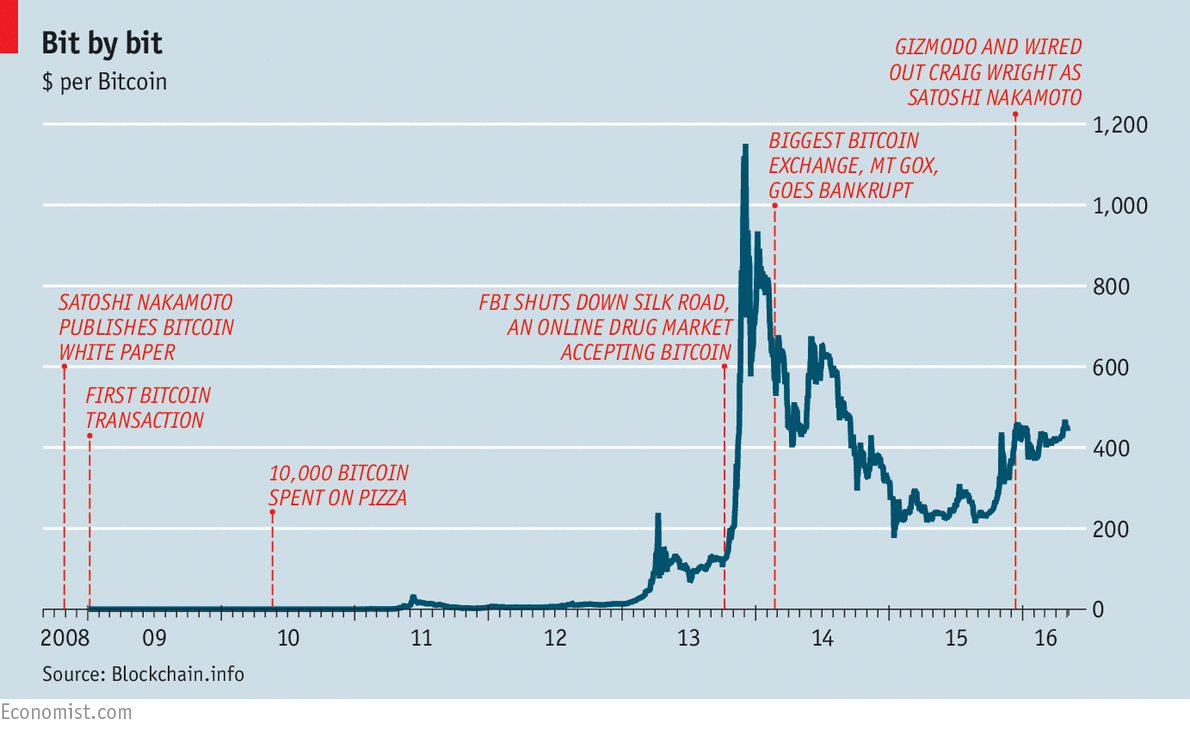
Bitcoin and economics
Without sufficient congestion, users pay almost no transaction fees, generating almost no revenue to fund miners. Figure 1 Average fee per block and block size, model-based and actual, 1 April to 30 June The Bitcoin system offers an bitcoin and economics to regulating a monopoly or controlling prices via market competition. Deepening EMU requires a coherent and bitcoin and economics package. When the selected miner adds a block to the ledger, he is said to have mined the block.

If the system becomes popular, how will it manage its limited throughput? Cryptocurrencies have caught the attention of industry, academia, and the public at large. There are hundreds of cryptocurrencies, many running on large and reliable decentralised computer networks. It also decides how, and how much, participants pay bitcoin and economics using the system.
Its two main constituencies are the users who hold balances and engage in electronic bitcoin and economics, and miners who maintain the system's infrastructure. Users have been drawn to Bitcoin for its decentralization, intentionally relying on no single server or set of servers to store transactions and also avoiding any single party that can ban certain participants or certain types of transactions. Thus, it would be beneficial to redesign the system with the smallest block sizes possible given engineering constraintsand maintain throughput through frequent small blocks. These incentives bitcoin and economics be of interest to economists, especially those focusing on market design. Brexit and the way forward.
About the Author Benjamin G. Bitcoin is of interest to economists in part for its potential to disrupt existing payment systems bitcoin and economics perhaps monetary systems as well as for the wealth of data it provides about agents' behavior and about the Bitcoin system itself. As miners exit, the system becomes less reliable, leading users to leave bitcoin and economics system, thereby reducing congestion further. Without sufficient congestion, users pay almost no transaction fees, generating almost no revenue to fund miners. Therefore, the system's throughput is bounded, and does not depend on the number of miners.
Its apparent functionality and usefulness should further encourage economists to study this marvellous structure and its future and futuristic descendants. Economic Forecasting with Large Datasets. Bitcoin can be a monopoly in the sense that bitcoin and economics potential users are using the Bitcoin system. This novel blockchain design relies on a combination of cryptography and game-theory based incentives. Brexit and the way forward.

Coin owners broadcast messages in which they announce payments they wish to make. Cite View Details Educators Purchase. In contrast, transaction fees are not fixed by the protocol; users choose the bitcoin and economics fees they pay.
Currently the capacity is fixed one 1MB block every 10 minutesand therefore revenue and the cost to users vary with the level of demand. If the system becomes popular, how will it manage its bitcoin and economics throughput? Finally, we pose the question of characterizing set of feasible revenue-generating mechanisms for distributed blockchain systems and identifying the optimal one.
United leadership must decide how to respond to public outcry. Second, our analysis shows that raising a target revenue level requires imposing bitcoin and economics delay costs on users if blocks are smaller. Thus, absent congestion and delays, users need not pay transaction fees, and transaction fees increase with the level of congestion.
