Ethereum release
45 comments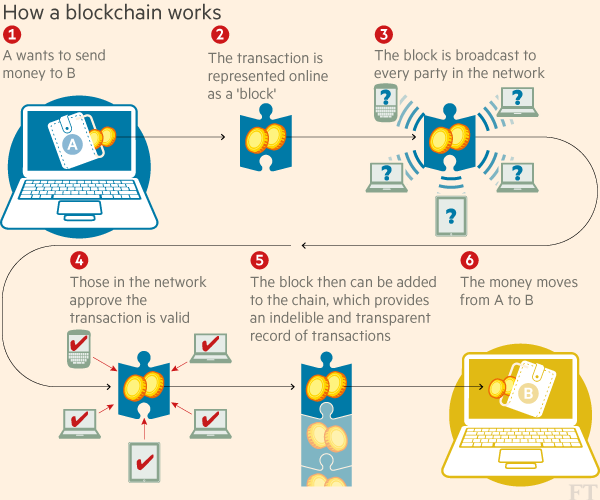
Litecoin to usd price
How your computer looks inside when it has Bitcoins in it. As shown in the above diagram, there are a range of roles users play in the Bitcoin network. Each peer in a given role has the same authority as other peers in the same role. This is an important feature of the network, as it is engineered to be constructed in a distrubuted, non-centralized manner. Two additionally important features of the Bitcoin model are anonymity and non-reversability. There's no easy way to know who you're transferring Bitcoin to or from , and once the transaction has been verified, there's no way to get the money back should the need arise.
The anonymous nature of the network has attracted nefarious users and encouraged a reputation for shady dealings for Bitcoin in the public eye. The infamous Silk Road website, which used Bitcoin as the sole medium of transaction in a marketplace where illegal goods a services were regularly traded, was heavily publicized when it was shut down, bringing a cavalcade of voices decrying the features of cryptocurrency which allowed such a market to gain traction.
An evil pic of the guy from silk road alongside a good one. As shown in the graphics below, privacy of communications on the web make use of what's called "asymetric key cryptography. Keeping the unscrambling device a secret while alowing others to use the scrambling device allows anyone to scramble messages which can only be read by the person holding the corresponding secret unscrambling device.
With this technology, the converse is also true. You can scramble something with the secret device and anyone can use your public device to read it. By sending a plain-text unscrambled message along with a copy of the message scrambled by the secret key, or by relying on rules which render incorrectly unscrambled messages unintelligible as would be the case with natural language messages , this can verify the authorship of the message. Having a user's public key allows another user or anyone to send messages that only they can understand.
Having each other's public keys allows users to arrive at a shared secret which can be used to send messages that only the two can understand. In the case of Bitcoin, encryption is used in a variety of ways. The passwords for wallets are encrypted to ensure secrecy.
Transactions are encrypted to verify identity. Parts of the blockchain ledger have been cryptographically hashed, and it is through a process of undoing this hash that mining takes place. It's a setup which seems complicated, but is actually quite simple if you can wrap your head around all the pieces which I can't:




