Bitcoin exchange rates usd to rand
21 comments
Jamaican bobsled dogecoin fundraiser
Many people new to Bitcoin in are just buying and holding it, but quite a few are getting involved with Bitcoin mining. There are two aspects of mining where you get money, the block reward and transaction fees. The block reward part is often called ' coinbase ', so you may see these terms used interchangably - not to be confused with the Coinbase exchange. Both of these rewards are given in Bitcoin.
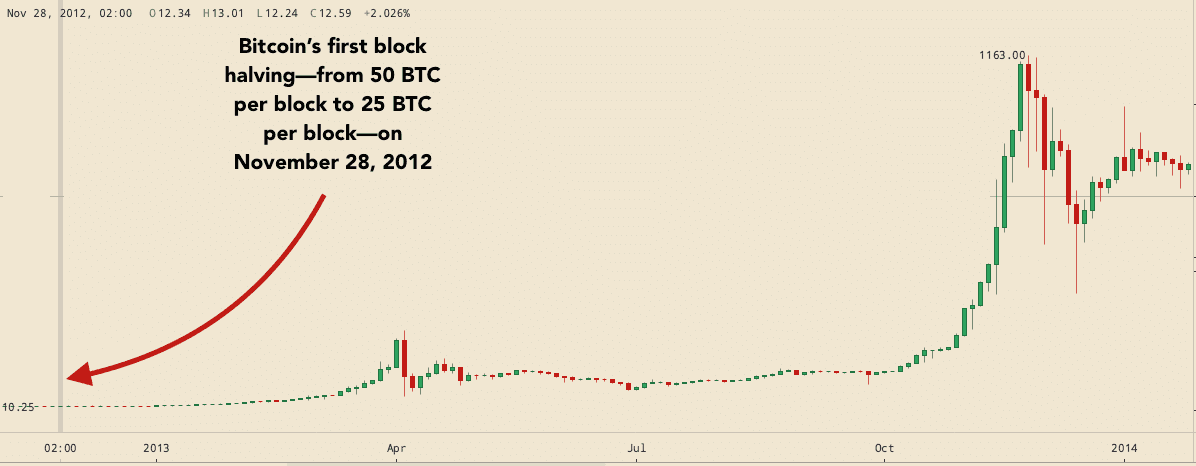
A Bitcoin block is 1MB in size, and Bitcoin transactions are stored inside these blocks each time someone sends Bitcoin, a new transaction is added. If a miner mines a new block, they're given a reward in the form of the block reward coinbase. This is the main incentive for Bitcoin miners, as the block reward is The block reward is halved every , blocks , which is approximately every 4 years.
You can see Bitcoin's code for this here. When Bitcoin was created the Block reward used to be 50 Bitcoin, and is now This decrease in block reward means that over time less and less new Bitcoin are created, which combined with increased demand is theorised to keep pushing Bitcoin's price up - so in principle the USD value of the block reward should be similar in 10 years time.
When the block reward has halfed 64 times, the block reward becomes 0. This block reward has to be claimed by miners, where they add it as the first transaction on a block. It has no inputs, but has an output to the miner's wallet address.
Here is an example on Block Explorer it should be the first transaction in the list. When sending Bitcoin, a fee needs to be paid by users - called a transaction fees. This exists to incentivise miners to include transactions in mined blocks. It's effectively a bidding war to get your transaction into a block, where whoever pays the highest fee is processed first.
A side effect of high demand for sending Bitcoin is more transactions being sent, and higher fees. This transaction fee is given to miners, so essentially - the more congested the Bitcoin network, the more money miners earn. This fee is essentially an extra payment sent with any Bitcoin transaction, and can be worked out by subtracting the outputs from the inputs of a transaction.
As the block reward coinbase reduces over time, if Bitcoin price doesn't increase at the same rate - these fees can provide an incentive for miners to continue mining.
So when you start mining, you might have a dream of getting say BTC in a week. You need to be aware that there is a huge number of people competing to create new blocks. By creating a new mining pool by yourself, the chance of getting this block reward is extremely low - although if you did get it by chance, you'd get a significant reward.
Instead, most miners join an existing mining pool - where they'd get a more steady income rather than having to wait years for a block reward to themself.
Mining pools are large groups of miners, where if any one of them creates a new block - the reward is shared based on how much work each miner contributed. Work is defined in hash power or hashrate, which in general means how many guesses can be made per second for the required hash.
The split between miners differs between mining pools, we're going to use Slushpool as an example in this guide - but you can see how other pools work here. Slushpool, which has For example if the goal is a hash that consists of 18 zeros, a miner can submit any time after they've found the first 8 - which would prove that they've done work to get this far.
They'd need to get all 18 zeros to win the block, but it would at least prove the miner is putting the effort in - and so they should be rewarded for it. The split is counted by the amount of work they have proved vs the total work proven by all the miners in the pool. Lets step back a moment though, now that we know how much work everyone's done - how is the reward distributed? The block reward for the miner who was lucky enough to find it would be very large, a lot more than the miner will see as a return from the pool in the short term.
What stops the miner taking that reward and leaving as if they were in their own pool? Well the blocks are pre-built by the pool. Everything except the nonce the value in the block that miners change to get a hash with a certain amount of preceding zeros must stay the same. One would assume that the pool can then just verify the nonce, and rewards wouldn't be awarded if the user changes the address as the hash won't pass when being verified by the pool - incentivising miners to follow the pool's rules although we are yet to find documentation on this.
This part is nice and simple. Whichever pool guesses a Block's hash first wins the Block reward. The more hashing power a pool has, the higher the probability that the pool will succeed. Extend this over a long period of time, then the reward split between pools should be similar to the share each pool has of total hashpower.
Slushpool for example, which currently has This site cannot substitute for professional investment or financial advice, or independent factual verification.
This guide is provided for general informational purposes only. The group of individuals writing these guides are cryptocurrency enthusiasts and investors, not financial advisors. Trading or mining any form of cryptocurrency is very high risk, so never invest money you can't afford to lose - you should be prepared to sustain a total loss of all invested money. This website is monetised through affiliate links.
Where used, we will disclose this and make no attempt to hide it. We don't endorse any affiliate services we use - and will not be liable for any damage, expense or other loss you may suffer from using any of these. Don't rush into anything, do your own research.
As we write new content, we will update this disclaimer to encompass it. We first discovered Bitcoin in late , and wanted to get everyone around us involved. But no one seemed to know what it was! We made this website to try and fix this, to get everyone up-to-speed! Click here for more information on these. All information on this website is for general informational purposes only, it is not intended to provide legal or financial advice. Jan 25th, Updated Jan 27th, Mining Many people new to Bitcoin in are just buying and holding it, but quite a few are getting involved with Bitcoin mining.
What are Block Rewards? What are Transaction Fee Rewards? How do pools distribute rewards? How does Slushpool distribute rewards? How are Rewards Split Between Pools? May 5th, What is the Antminer Z9 Mini? Written by the Anything Crypto team We first discovered Bitcoin in late , and wanted to get everyone around us involved. Never invest money you can't afford to lose.