Cara cepat mendapatkan bitcoin gratis
24 comments
How to get started with bitcoin mining
Implementing blockchain for cognitive IoT applications, Part 1. How are these two technologies being used to build end-to-end secure and automated solutions? Internet of things IoT solutions are being successfully adopted in many different industries, such as healthcare, warehousing, transportation, and logistics.
Current centralized, cloud-based IoT solutions may not scale and meet the security challenges faced by large-scale enterprises. The use of blockchain as a distributed ledger of transactions and peer-to-peer communication among participating nodes can solve such problems.
This article provides an overview of blockchain-enabled IoT solutions and demonstrates how to use the IBM Blockchain platform for an IoT application in a multi-partner environment.
Blockchain refers to a distributed ledger where a list of transactions is stored in multiple participating servers rather than on a central transaction server. Each participant in the blockchain network is granted access to an up-to-date copy of this encrypted ledger so they can read, write, and validate transactions.
Refer to the Related topics for more details on blockchain and how IBM is contributing to developing a blockchain for business. While the key blockchain usage scenarios are in the financial domain, blockchains have recently gained a lot of attention in IoT solutions. Blockchain can significantly help in achieving the vision of decentralized IoT, facilitating transactions and coordination among interacting devices.
IoT has introduced huge opportunities for businesses and consumers, especially in the areas of healthcare, warehousing, transportation, and logistics. IoT solutions involve a complex network of smart devices, and IoT provides the opportunity to develop new services based on cloud-enabled connected physical devices—from machines and cars to home appliances.
While IoT adoption is growing significantly, some key challenges need to be addressed to make IoT solutions scale and support the ever-growing demand for more and more connected devices.
IoT solutions must address the security and privacy concerns around these devices and the data they collect. Some of these challenges are:. Blockchain technology and IoT offer a new world of promise, and can be leveraged to address the problems described above.
For example, connected devices could communicate directly with distributed ledgers. Data from those devices could then be used by smart contracts to update and validate the data and subsequently deliver it to all interested participants in the business network. This would reduce the need for human monitoring and actions, and promote trust in the data generated by the devices. Decentralized blockchain networks can also improve the security of IoT solutions by executing predefined smart contracts and implementing specific consensus mechanisms that eliminate actions from compromised devices.
Data from IoT devices can now be integrated with the private blockchain ledgers and shared transactions with high security. The combination of IoT and blockchain is creating a lot of new possibilities for using smart devices in the asset management cycle. As assets go through the various phases of their lifecycle, devices monitor different aspects and integrate the data from the assets into a blockchain of the business participants to provide real-time, trusted data.
Similarly, the quality and price of the food items can be determined based on the real-time refrigeration data used in transportation. IBM along with Samsung demonstrated the use of blockchain in autonomous washing machines that can reorder detergent and replacement parts, and arrange for after-sales service using smart contracts. Several consortiums such as Chain of Things and start-up companies such as Filament have demonstrated other smart ways of leveraging distributed ledgers in IoT networks to automate the end-to-end processes and integration with business participants.
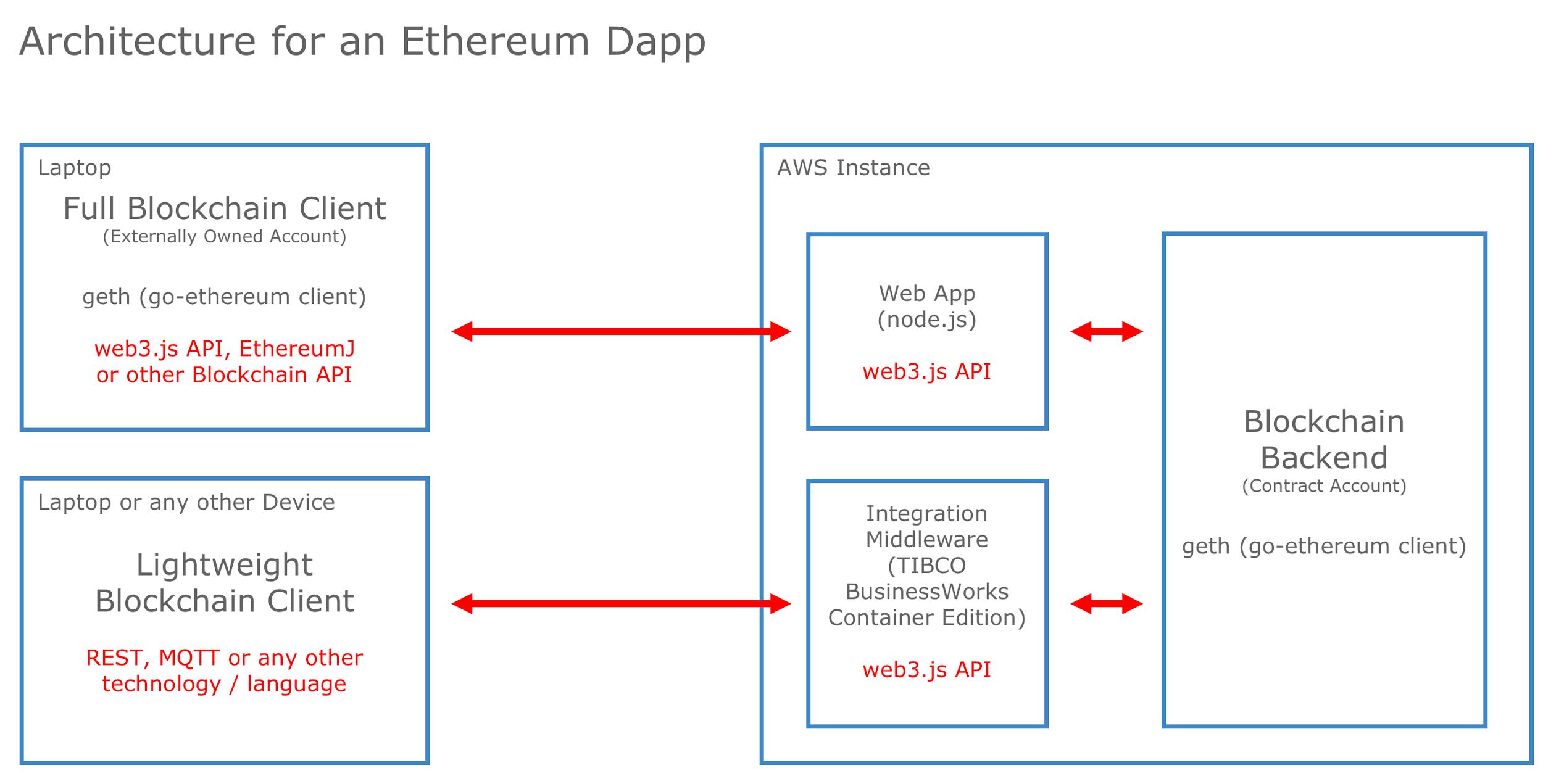
The table below lists some blockchain-based IoT use cases for different industries:. View image at full size. Blockchain proxy in the Watson IoT Platform sends the data to the chaincode based on a pre-defined configuration. Smart transactions are executed in IBM Cloud based on the device data. IBM Blockchain provides the private blockchain infrastructure for developing blockchain-enabled solutions.
The Blockchain service is an implementation of Hyperledger Fabric. It provides the following:. Smart contracts form the core of blockchain-based solutions and encapsulate the business logic.
Each invocation of a smart contract is recorded as a blockchain transaction. Smart contracts need to be registered with blockchain services using pre-defined APIs. Contract API needs to be implemented by a smart contract developer. It has three main functions: Init , Invoke , and Query. Applications can securely register users and submit transactions using this API. A list of supported operations is shown in the table below:. IBM-Blockchain-js is a Node.
It provides functions in the easy-to-use Node. The HFC is designed to be used in the Node. For more details, see these resources:. The client application is responsible for providing the required data to stakeholders to meet their business needs and provide a rich user experience. Client applications need to use the blockchain API as provided for the smart contracts to interact with the business ledger.
These applications can also process the events generated by the blockchain components. The IBM Watson IoT Platform receives data from all of the registered devices and processes that data into the required format for integration with blockchain.
Developers need to have several skills to develop end-to-end IoT applications using these services. Developers need to set up a private blockchain based on the IBM Blockchain service.
Refer to the IBM Cloud documentation on setting up private blockchain services. Develop and deploy smart contracts in blockchain based on device data. A contract can be set up to reject a shipment or reduce a price if the temperature of the container measured by sensors exceeds a certain threshold.
Follow the documentation to add the devices to the Watson IoT Platform. When successfully added, the Devices page on the Watson IoT dashboard will look like this:. As you can see, there is huge potential for developing applications using blockchain in IoT solutions, and this combination can solve some of the key problems that limit adoption of IoT, such as security and scalability.
A distributed ledger with embedded smart contracts can improve security and trust, and automate complete processes comprised of multiple business partners. There are, however, a few challenges that need to be overcome. One of the key challenges of blockchain-based IoT applications is the limited computing power of many IoT devices.
Encryption and verification of blockchain transactions can require considerable processing power, which may not be available in low-end devices.
And use of more processing power can increase both the energy consumption and the cost of the solution. Sign in or register to add and subscribe to comments. Implementing blockchain for cognitive IoT applications, Part 1 Integrate device data with smart contracts in IBM Blockchain How are these two technologies being used to build end-to-end secure and automated solutions?
This content is part of in the series: Implementing blockchain for cognitive IoT applications, Part 1 https: This content is part of the series: Implementing blockchain for cognitive IoT applications, Part 1 Stay tuned for additional content in this series.
Comments Sign in or register to add and subscribe to comments. Subscribe me to comment notifications. Integrate device data with smart contracts in IBM Blockchain. Lack of visibility is a key problem in the supply chain. Even when data on the processes is available, it's not reliable enough that it should trigger concrete actions. Blockchain can help solve some of the key problems in the supply chain: It can ensure proper access control for data shared among participants in the supply chain.
A supply chain with continuous, real-time access to reliable, shared data in blockchain can be optimized more efficiently than that of traditional supply chains. Concrete supply chain use cases based on Blockchain and IoT include: Tracking food items from farm to packaging and shipping Identifying contamination and reducing food waste in the supply chain These use cases make use of location, refrigeration, soil, and weather data streams in an IoT blockchain to make all relevant data available to participants in real time.
The automotive industry is one of the leading industries in the adoption of blockchain-based IoT solutions. Blockchain-based solutions are being used to provide real-time information and to execute transactions among key business partners—manufacturers, auto financing companies, insurers, service providers, regulators, and customers. In addition to the adoption of blockchain in auto supply chains, sensor data from various vehicle parts are integrated with blockchain to make real-time decisions and transactions involving services and payments.
For example, Toyota has started using blockchains to track the thousands of parts that travel through various countries, factories, and suppliers to manufacture a single car. Blockchain has disruptive potential for the energy industry. Blockchain-supported IoT networks of energy grids enable peer-to-peer transactions of energy.
In one application, excess rooftop solar energy is sold to other users who need it—all of which is paid for and recorded through a blockchain. Startup companies like Filament are also building mesh networks of smart devices that monitor energy grids and fix any issues that arise as quickly as possible. Use of blockchain can help improve the security of private patient data that comes from medical monitoring devices.
Data is stored securely in a distributed ledger, and participants are given access based on smart access rules that are set in the blockchain for example, approval from 3 or more parties. This can also help to provide real-time trusted patient data for required participants such as insurance providers or third-party administrators and help them release payments based on more accurate data.
IoT-enabled technologies are being used in smart cities and intelligent buildings to improve operations, security, and the experience of residents. A huge number of devices and sensors are being used to monitor and manage these facilities.
A blockchain-enabled IoT network can secure devices and the data collected from them. All facility management suppliers can participate in a private blockchain to provide timely service and automate the payment process based on the actual work done or the quality of service. Blockchain technology also helps improve the management of devices and the security of the data flow in the network. It enables access control of the data that flows to different participants, allows the exchange of data among participants, and provides the necessary payment services that are integrated with the flow of the data.
The chain endpoint returns information about the current state of the blockchain. This API returns a list of all existing network connections for the target peer node. The list includes both validating and non-validating peers.